Introduction
Every day we solve problems, and every day, we come up with different strategies and solutions to various problems, and ideation is the fundamental stage in problem-solving. The word ideation might sound new, but the word has been around since the 1800s. When broken down, the term stems from the combination of the words 'idea' and 'creation'.
Ideation can often be mistakenly interchanged with the terms like brainstorming and idea generation. While these are not far from the truth, these are simply parts of a more comprehensive process, which is ideation in itself.
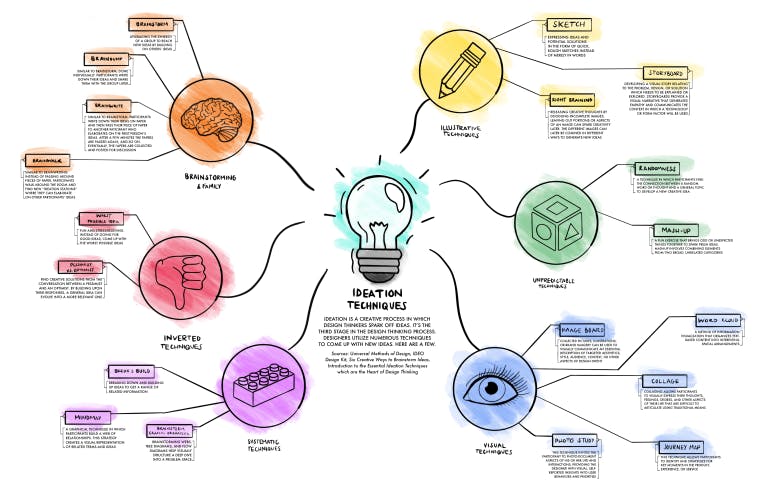
According to Vocabulary.com, ideation is defined as 'the process of forming and relating ideas' [1]. There's a bit more to this definition, as ideation also involves selecting the best-generated ideas, and developing them further, both of which are essential.
Ideation is a creative process of generating, developing, and communicating ideas. At this point, it is essential to note that these ideas don't have to be completely new. Ideation can be done to solve specific problems, look into new ways of implementing a solution, or even collect feedback and evaluate ideas [2].
From this understanding, ideation can begin to be understood to not be just a one-time idea generation. This process phase can be divided into three stages:
The generation stage
The selection stage
The development stage.
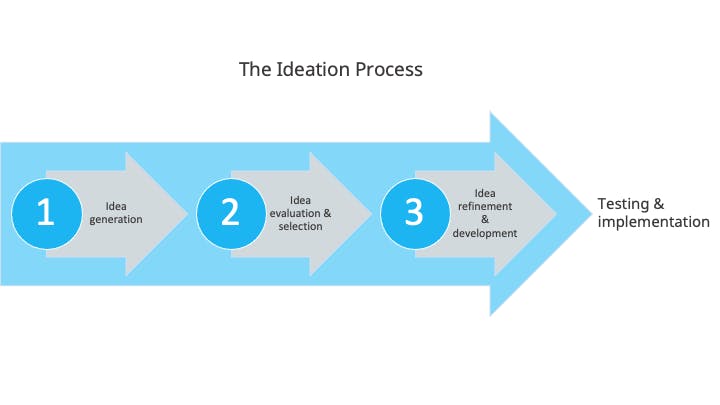
Ideation is not just a one-time idea generation...
[2].
Ideation starts with idea generation, but the process starts earlier when you identify and define the problem, specific strategies, or opportunity. In facilitating the flow of the ideation phase, various activities are carried out to achieve these.
Ideation doesn't stop at idea(s) generation; it also involves evaluating, refining, selecting, and developing ideas. After all, what is an idea worth unless implemented and making it work?
[2].
Why Ideation is Important
Some specific benefits of ideation are:
It can increase the opportunities for innovation: Generally speaking, ideas are good when they have the potential to turn into something that brings value. The good thing about ideation is that tons of ideas can be generated, and when there are more, there is an increased chance of having more good ones.
It can bring together different perspectives and ways of thinking: The purpose of an ideation phase and its expected outcome influences the type of ideators brought together (especially in group sessions). During ideation, diversity in thought and knowledge reveals new areas of exploration.
When we bring together diversity in terms of experiences and knowledge, we can look through a fresh lens
[2].It helps to develop and refine ideas into better ones: An effective ideation process isn't a 'spray-and-pray' system. While generating ideas with the hope that one is the winner sometimes works, this isn't the best approach to be relied on. An ideation process planned and prepared in advance to solve a specific challenge or aimed for a particular goal helps challenge existing ideas and makes it easier to select the most promising ones.
An environment to develop and refine the best ideas is fundamental to a good ideation process.
It helps to prioritize ideas and pick the most promising ones: A well-planned ideation process helps to prioritize ideas and choose those that have the highest potential for implementation. Evaluating ideas and choosing which ones to take further can become complicated, especially if you are dealing with more complex ideas. So, finding consistent criteria to evaluate and prioritize ideas is essential.
It encourages an open, innovative culture: As discussed earlier, ideation is not just about the ideas. It’s also about the culture it nurtures. When people are encouraged to participate and transparently speak their minds, they will feel more connected to the cause and will have a sense of belonging because they can actively contribute to the bottom line and their ways of working.
Key challenges to ideation
Awareness of some challenges in doing ideation in practice is essential. These challenges can arise at any stage of the ideation process. One can choose and develop the best idea but still fail in delivery. Here are a few challenges that can be faced during ideation and the likely way of tackling them:
Functional fixedness: Functional fixedness is a term generally describing the inability to realize that something with a specific function can also be used with different functions. This kind of cognitive bias can affect our ability to think creatively and come up with new ideas. To overcome this in the context of ideation, try asking questions like “Why not” or “What if”.
Déformation professionnelle: This term borrowed from French is another cognitive bias that shows how expertise is not always a recipe for success. That’s why bringing the right people into an ideation process is very important. And by “right”, this doesn’t mean the best, most experienced in the field, but diverse people with different backgrounds, skills, and knowledge.
It can be chaotic: Ideation is often associated with the group sessions, the post-its on the walls, and the fun-looking events. While these can have their time and place, the outcome of such activities can be chaotic and messy, and a lot of good ideas are often lost in the process. With an ideation tool, one can transparently share ideas, gather feedback, refine, evaluate, and further develop them. Instead of trying to reinvent the wheel, an ideation tool can dramatically increase knowledge sharing and allow people to keep on building on top of the existing one.
Critical success factors for ideation
Now that the significant challenges of ideation are analyzed let’s see what one can do differently to increase the odds of success in an ideation process.
Align ideation with strategic goals
Have and follow a structured and methodical approach
Ask the right questions
Get the right people
Express and test assumptions behind the ideas
Love the problem, not the idea
Eliminate barriers
Conclusion
Ideas are the starting point of every innovation, and while having many ideas to choose from is great, if nothing happens with those ideas in terms of selection, development, and implementation, again, there is no innovation.
So, even though ideation might sometimes get a bad reputation, the problem is usually not with ideation per se but with the lack of systematic processes to get from vague ideas to implement solutions that serve the organization’s overall goals.
That being said, commit to the process, take it step by step, and systematically work towards implementing your ideas.
References
Vocabulary.com. (n.d.). Ideation. In Vocabulary.com Dictionary. Retrieved July 23, 2023, from https://www.vocabulary.com/dictionary/ideation
Porumboiu, D. (n.d.). The Complete Guide to Ideation. The Complete Guide to Ideation. https://www.viima.com/blog/complete-guide-to-ideation?hs_amp=true

